Introduction
Ever wondered how hackers access other users' shopping carts? In this lab, I explored a critical authorization flaw in the OWASP Juice Shop application using Burp Suite. By simply manipulating HTTP requests, I was able to bypass security mechanisms and access another user's cart data.
This type of vulnerability is more common than you'd think—and it's exactly why understanding these attacks is crucial for building secure applications.
Tools Used:
- Burp Suite (Proxy & Interceptor)
- Firefox Browser
- OWASP Juice Shop
Setting Up the Environment
First, I accessed the Juice Shop application at http://juice-shop.herokuapp.com. The original lab IP wasn't reachable, so I used the publicly hosted version instead.
I created a new user account and logged in:
 OWASP Juice Shop dashboard after successful login
OWASP Juice Shop dashboard after successful login
Configuring Burp Suite as a Proxy
The magic of Burp Suite lies in its ability to intercept and modify HTTP traffic. Here's how I set it up:
Step 1: Configure the Proxy
I launched Burp Suite and configured the browser proxy settings:
- HTTP Proxy: 127.0.0.1
- Port: 8080
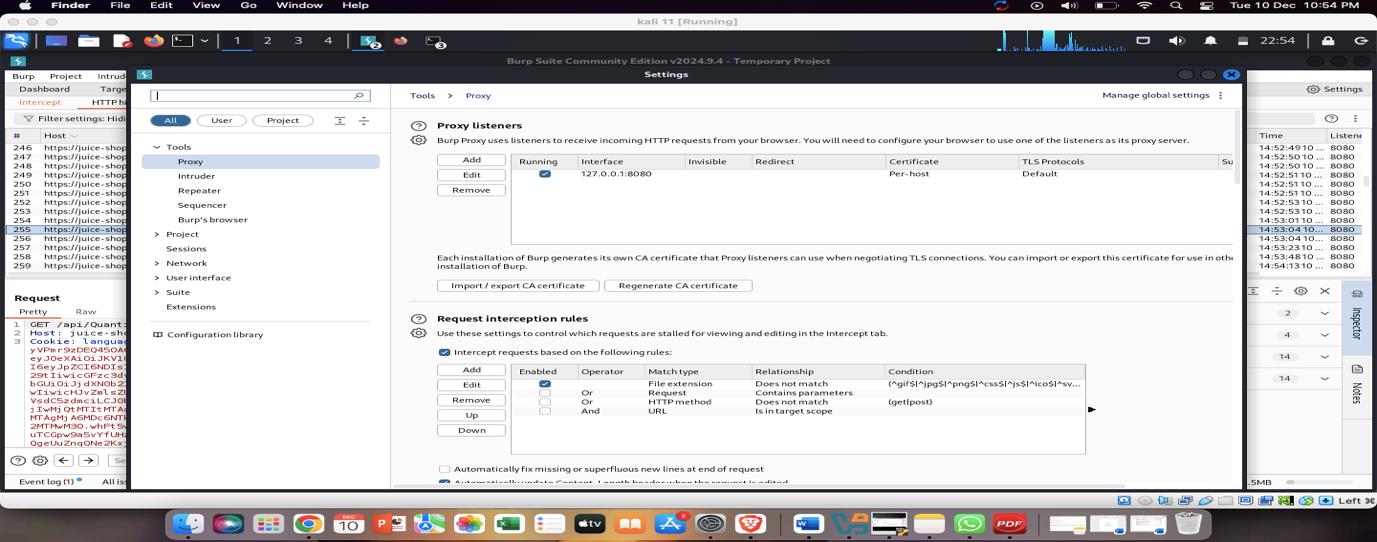 Burp Suite proxy configuration showing the listener on port 8080
Burp Suite proxy configuration showing the listener on port 8080
Step 2: Import the CA Certificate
To avoid SSL/TLS errors when intercepting HTTPS traffic, I imported Burp Suite's CA certificate:
- Navigate to
http://burpsuite/cert - Download the certificate
- Import it into Firefox's certificate manager
Step 3: Enable Interception
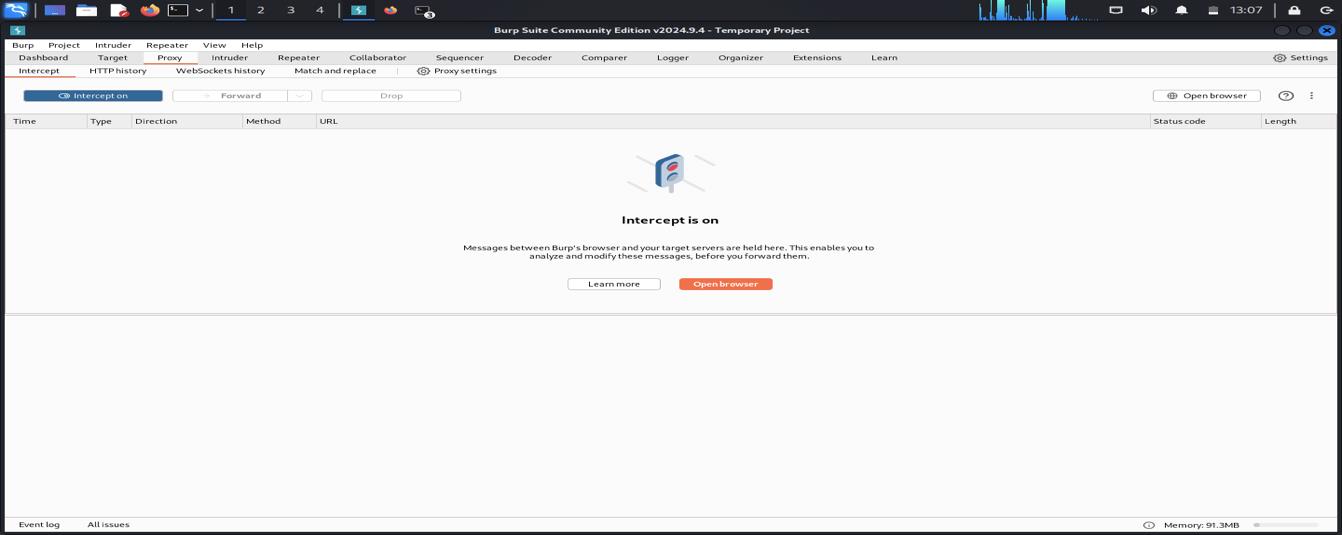
With the proxy configured, I turned on the Interceptor to capture requests:
 Burp Suite with Intercept mode turned ON
Burp Suite with Intercept mode turned ON
The Exploit: Accessing Another User's Cart
Here's where it gets interesting. The vulnerability I discovered is a classic Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR).
How It Works
When you view your shopping cart in Juice Shop, the application sends a request like:
GET /rest/basket/19 HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...
The basketId (19 in this case) identifies YOUR cart. But what if we change it to someone else's ID?
Step 1: Intercept the Request
After adding an item to my cart, I intercepted the GET request in Burp Suite:
 Original request showing basketId=19 and the Authorization Bearer token
Original request showing basketId=19 and the Authorization Bearer token
Step 2: Modify the basketId
I changed the basketId from /rest/basket/19 to /rest/basket/1:
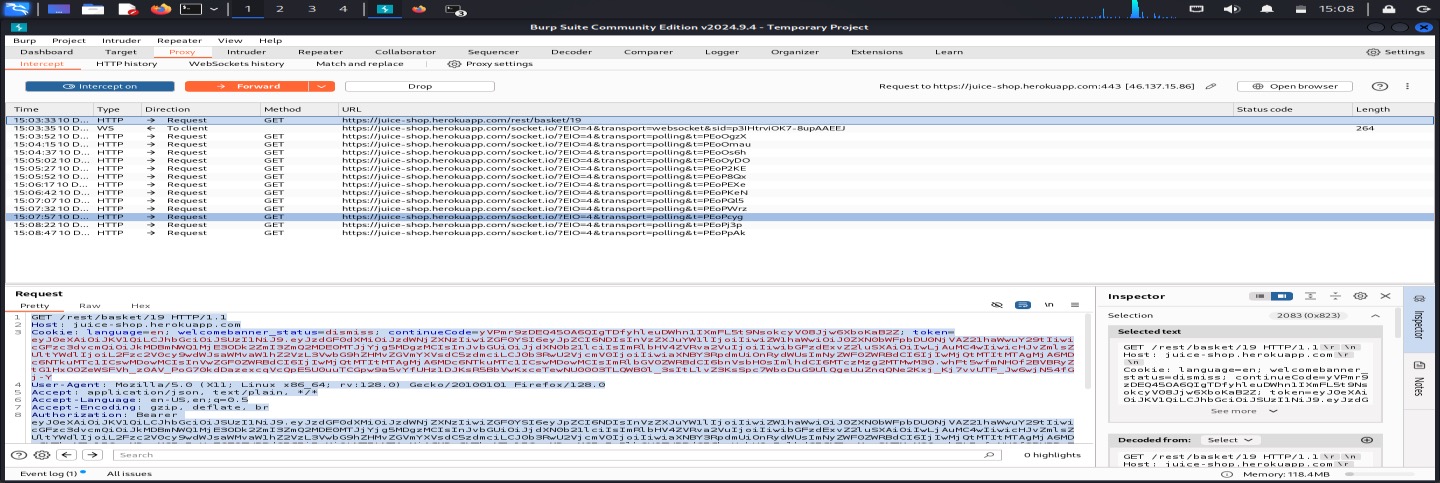 Modified request with basketId changed to 1
Modified request with basketId changed to 1
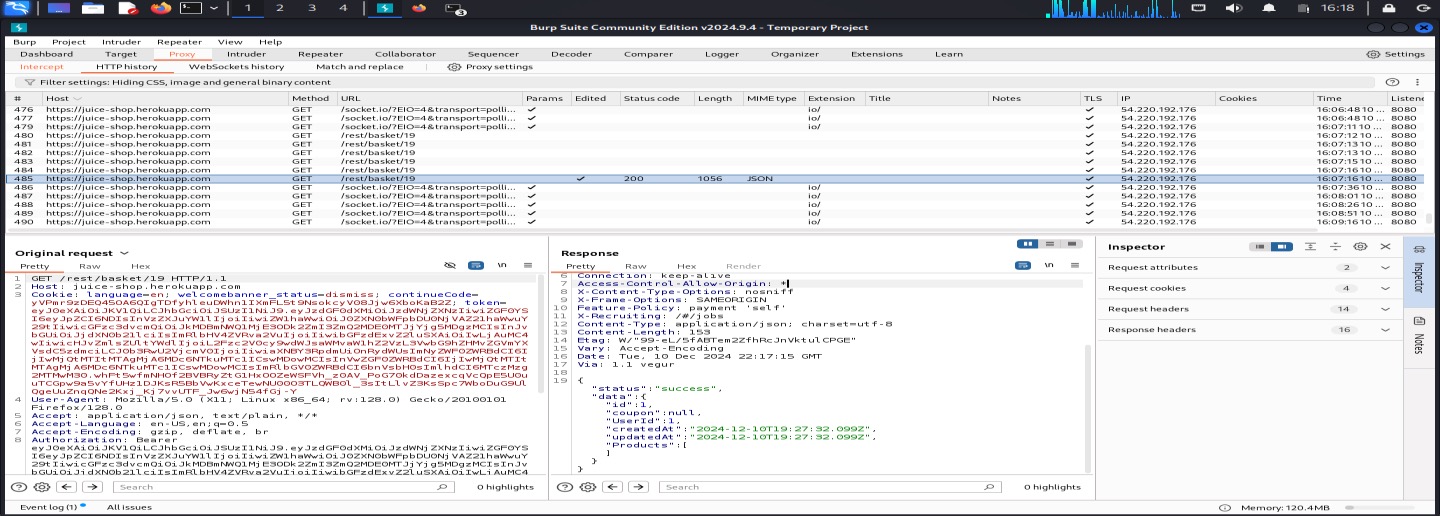
Step 3: Forward and Observe
After forwarding the modified request, I checked the HTTP History tab. The server responded with... another user's cart contents!
 Server response showing successful unauthorized access to basketId=1
Server response showing successful unauthorized access to basketId=1
Boom. I just accessed another user's shopping cart without any authentication for that account.
Going Further: Forged Reviews
To explore additional vulnerabilities, I attempted the "Forged Review" challenge from the Juice Shop scoreboard. This involved submitting a product review as another user.
 WebSocket response showing successful forged review challenge completion
WebSocket response showing successful forged review challenge completion
The success message confirmed that I could impersonate other users for review submissions as well.
Why This Vulnerability Exists
The root cause is simple: the server trusts the basketId without verifying user ownership.
The Flawed Logic
User requests → GET /rest/basket/{id}
Server checks → Is the user authenticated? ✅
Server DOESN'T check → Does this user OWN this basket? ❌
The application verifies that you're logged in, but it doesn't verify that the resource you're requesting actually belongs to you.
How to Fix This
If you're a developer, here's how to prevent this vulnerability:
1. Server-Side Ownership Verification
// BAD - No ownership check
app.get('/rest/basket/:id', (req, res) => {
const basket = getBasket(req.params.id);
res.json(basket);
});
// GOOD - Verify ownership
app.get('/rest/basket/:id', (req, res) => {
const basket = getBasket(req.params.id);
if (basket.userId !== req.user.id) {
return res.status(403).json({ error: 'Forbidden' });
}
res.json(basket);
});
2. Use Non-Predictable Identifiers
Instead of sequential IDs (1, 2, 3...), use UUIDs:
/rest/basket/19 → Predictable, enumerable
/rest/basket/a7f3b2c1-9d8e-4f5a-b6c7-d8e9f0a1b2c3 → Much harder to guess
3. Implement Proper Session Validation
Tie resources to the authenticated session and validate on every request.
Challenges I Encountered
Challenge 1: Connection Issues
The lab's IP address (http://10.6.6.12:300) wasn't reachable.
Solution: Used the publicly hosted Juice Shop at https://juice-shop.herokuapp.com
Challenge 2: Certificate Errors
HTTPS traffic couldn't be intercepted due to certificate validation errors.
Solution: Downloaded and imported Burp Suite's CA certificate into Firefox's certificate manager.
Key Takeaways
- Never trust client-supplied IDs - Always verify resource ownership on the server side
- IDOR vulnerabilities are everywhere - This is consistently in the OWASP Top 10
- Burp Suite is incredibly powerful - Essential tool for any security professional
- Predictable IDs are dangerous - Use UUIDs or other non-enumerable identifiers
Conclusion
This lab demonstrated how a simple manipulation of an HTTP parameter can lead to unauthorized access. The OWASP Juice Shop is an excellent platform for learning web security, and Burp Suite is the go-to tool for intercepting and analyzing web traffic.
Authorization bypass vulnerabilities like this can lead to:
- Data breaches
- Privacy violations
- Regulatory compliance issues
- Loss of user trust
As security professionals, understanding these attacks helps us build more secure applications.
Technologies Used
- Burp Suite - Web application security testing
- OWASP Juice Shop - Vulnerable web application for learning
- Firefox - Browser with proxy configuration
- HTTP/HTTPS Interception - Traffic analysis and modification